NF Lactose Concentration Case Study
Download Full Case Study
Overview
The objective of this study was to examine the flux, total organic carbon (TOC) rejection, and calcium rejection performance of Synder’s NFX and NFS membranes, with acid whey UF permeate used as the incoming feed stream. These results will determine the potential for NFS to be used in the dairy industry for applications such as lactose concentration and demineralization, with specific focus on calcium removal.
Experimental
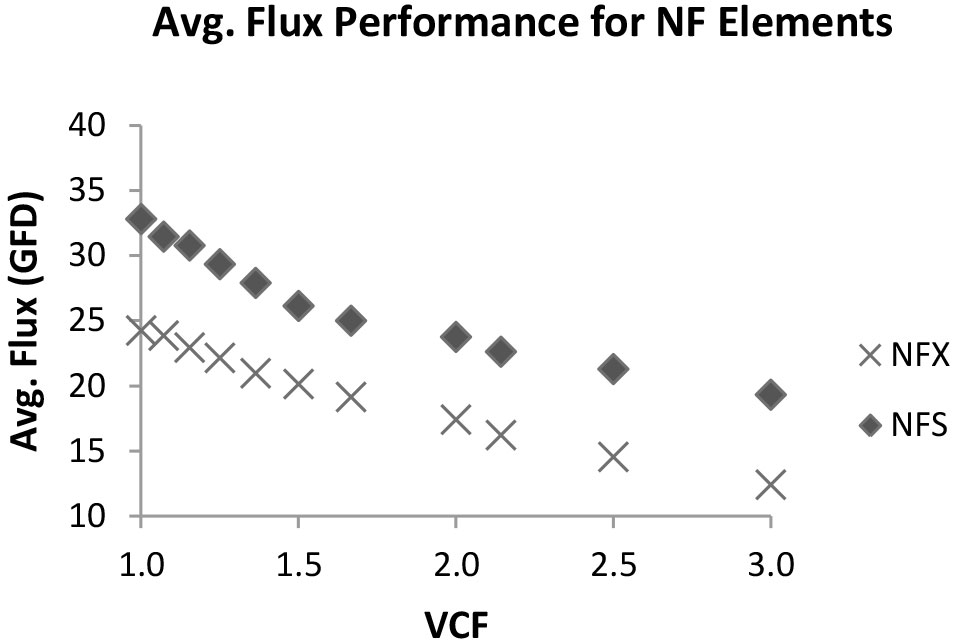
Two independent trials were tested with Synder’s NFX and NFS membranes in 2540 spiral wound element modules. Acid whey UF permeate generated from Synder’s ST 2540 spiral wound elements was used as the incoming feed stream. Elements were tested at 440 psi with a feed flow rate of 2 gpm at 25°C. Permeate flux and calcium rejection was measured from 1x to 3x volumetric concentration factor (VCF).
| Table 1: Acid Whey Powder Composition | |
| Description | Specification |
| Ash | 10.5% max |
| Fat | 1.2 max |
| Moisture | 5.0 max |
| pH | 4.5-5.0 |
| Protein (as is) | 11% min |
| Sediment | 15.0 mg max |
| Titratable Acidity | 0.30% min |
Results
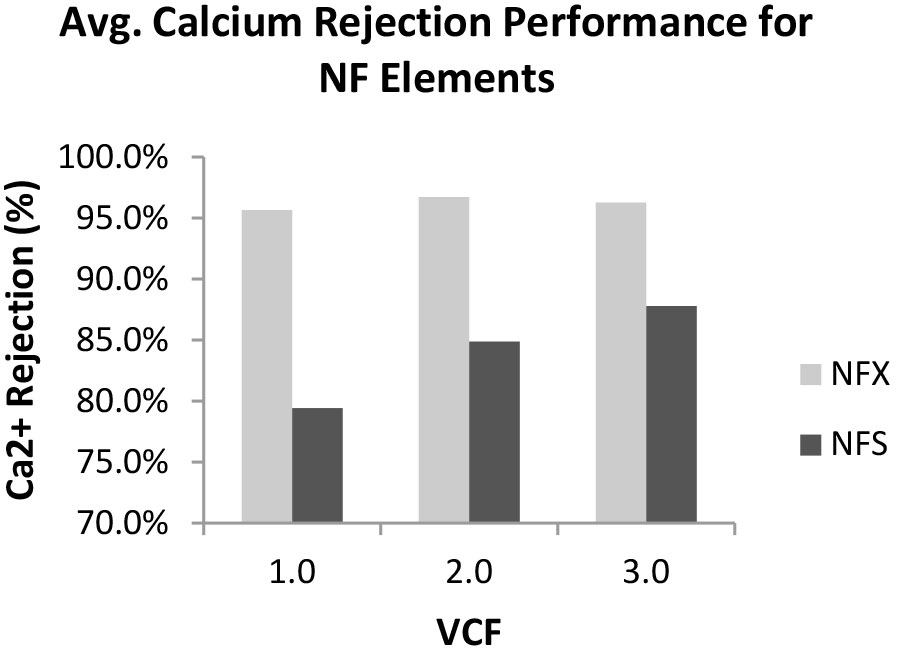 Figure 1: Average calcium rejection performance for Synder’s NFX and NFS 2540 elements obtained up to 3x VCF.
Figure 1: Average calcium rejection performance for Synder’s NFX and NFS 2540 elements obtained up to 3x VCF. 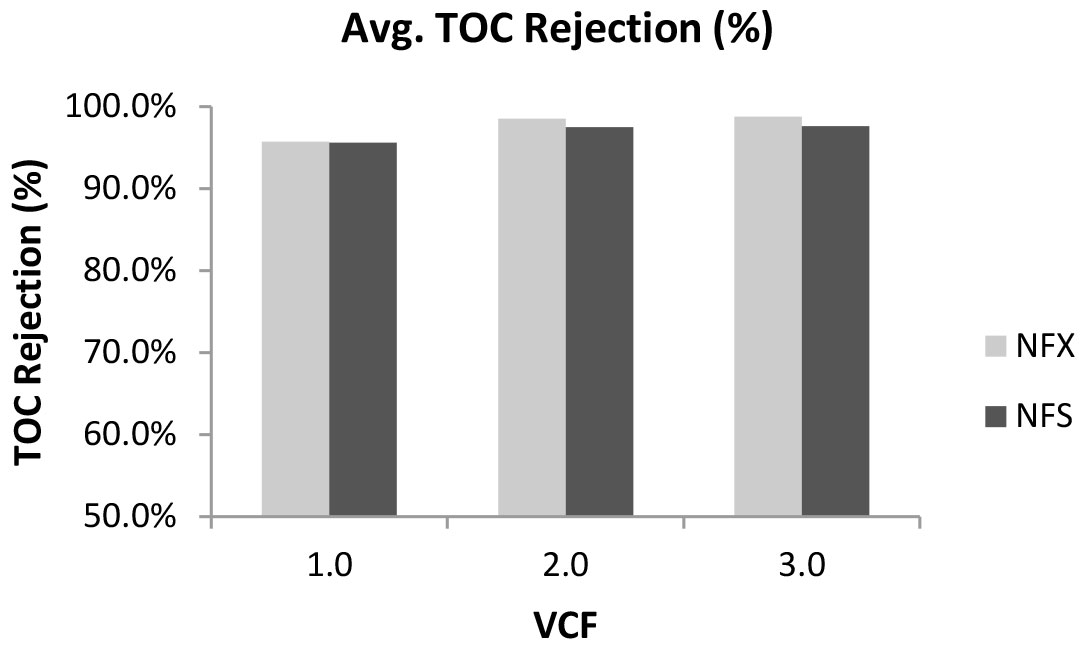 Figure 3: Average TOC rejection performance for Synder’s NFX and NFS 2540 elements obtained up to 3x VCF.
Figure 3: Average TOC rejection performance for Synder’s NFX and NFS 2540 elements obtained up to 3x VCF. Conclusion
The results of this study indicate that Synder’s NFS membrane shows superior flux and higher calcium passage compared to NFX, in a feed stream composed of acid whey UF permeate. The considerable difference in calcium rejection performance between the two membrane types shows the benefit for NFS to product higher-quality lactose. TOC rejection performance data was also comparable for both membrane types. These results indicate the potential for the NFS membrane to be used for lactose concentration and decalcification applications.
questions? Fill out this form. We’ll contact you within 24 hours!
CASE STUDY
SEAWATER SULFATE REMOVAL

As global demand rises, nanofiltration technology has become essential throughout the oil and gas industry by improving the efficiency of waterflooding… //READ MORE
Applications
Resources
MEMBRANE RESOURCES
- Definition of a Membrane
- Membrane Materials: Organic vs. Inorganic
- Pressure-Driven Membrane Filtration Processes
- Concentration Polarization in Pressure-Driven Processes
- Degrees of Membrane Separation
- Flux Behavior in Membrane Processes
Module Configurations & Processes
-> View all membrane resourcesTUTORIALS