Cross Flow Membrane Operations
Dead end filtration
Dead end filtration is when flow is applied perpendicular to the membrane surface. Particles smaller than the effective pore size pass through as filtrate, and particles that are larger build up as a cake layer on the membrane surface.Cross flow filtration
Cross flow filtration is when the flow is applied tangentially across the membrane surface. As feed flows across the membrane surface, filtrate passes through while concentrate accumulates at the opposite end of the membrane. The tangential flow of the membrane creates a shearing effect on the surface of the membrane, which in turn reduces fouling.Advantages of cross flow versus dead end
Because cross flow removes build up from the surface of the membrane, the permeate flux does not drop as fast when compared to dead end filtration. Cross flow technology also provides the benefit of an improved membrane lifespan by helping to prevent irreversible fouling.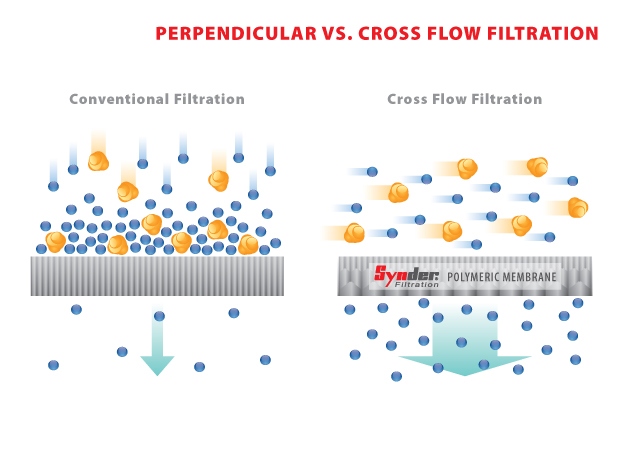
CASE STUDY
Applications
questions? Fill out this form. We’ll contact you within 24 hours!
Resources
MEMBRANE RESOURCES
- Definition of a Membrane
- Membrane Materials: Organic vs. Inorganic
- Pressure-Driven Membrane Filtration Processes
- Concentration Polarization in Pressure-Driven Processes
- Degrees of Membrane Separation
- Flux Behavior in Membrane Processes
Module Configurations & Processes
-> View all membrane resourcesTUTORIALS









