Amoxicillin Removal via NF Case Study

Experimental
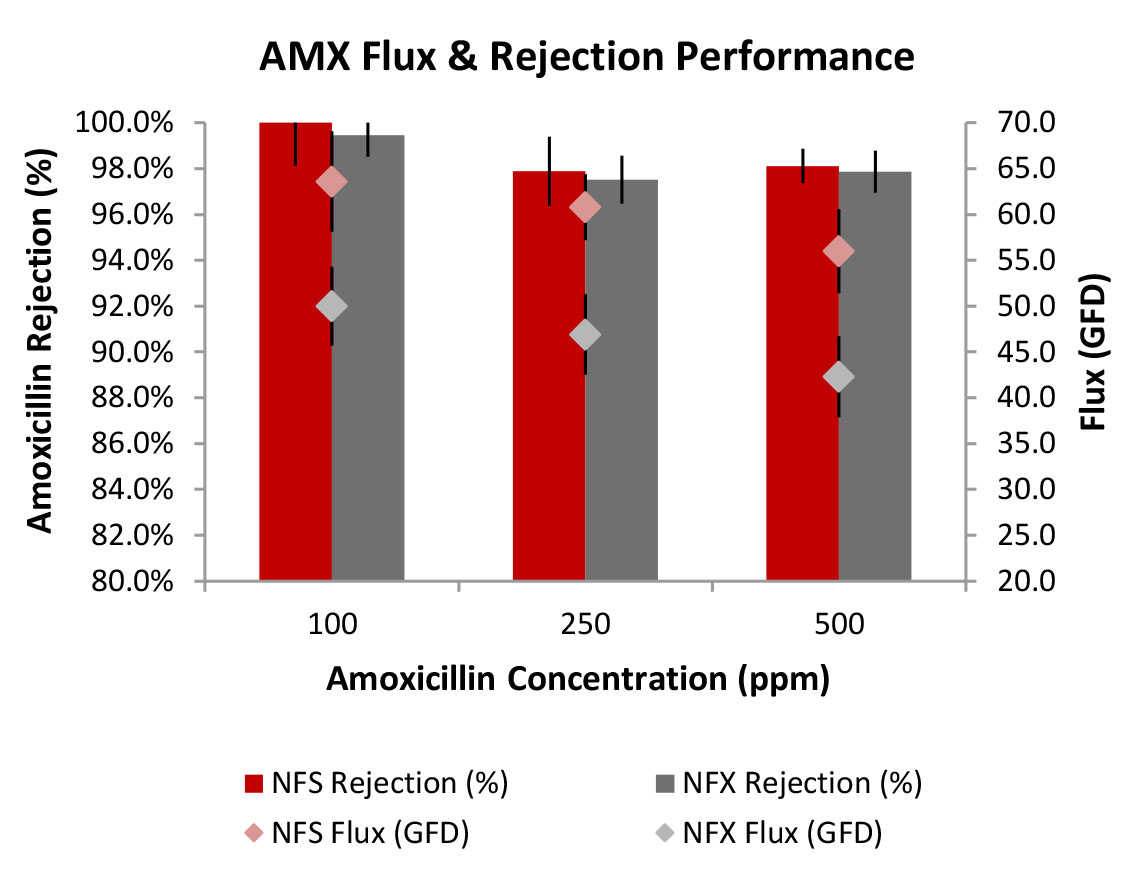
Synder’s NFS and NFX flat sheet membranes were tested at amoxicillin concentrations ranging from 100ppm to 500ppm. The membranes were tested at 120psi with a feed flow rate of 0.5gpm at 25°C. Permeate flux and TOC rejection were measured for all samples.
Results
NFS exhibited a 21-24% increase in flux over NFX throughout the duration of the test. This membrane also performed slightly higher than NFX in terms of amoxicillin rejection at all concentrations. Figure 1 shows the flux and rejection performance from 100 to 500ppm for both membrane types.
Conclusion
Based on the flux and rejection performance, both NFS and NFX nanofiltration membranes are viable options for antibiotic removal in wastewater treatment applications. NFS offers a significant improvement in terms of flux, in addition to the slight advantage with regards to amoxicillin rejection.
Further testing can be done to assess performance of antibiotic rejection in a wastewater feed solution.
questions? Fill out this form. We’ll contact you within 24 hours!
CASE STUDY
SEAWATER SULFATE REMOVAL

As global demand rises, nanofiltration technology has become essential throughout the oil and gas industry by improving the efficiency of waterflooding… //READ MORE
Applications
Resources
MEMBRANE RESOURCES
- Definition of a Membrane
- Membrane Materials: Organic vs. Inorganic
- Pressure-Driven Membrane Filtration Processes
- Concentration Polarization in Pressure-Driven Processes
- Degrees of Membrane Separation
- Flux Behavior in Membrane Processes
Module Configurations & Processes
-> View all membrane resourcesTUTORIALS