Pressure Drop and its Effect on Membranes
Pressure drop is defined as the loss of pressure between the inlet and outlet of a membrane system, housing (pressure vessel), or element. When a pressure drop exceeds the normally reported value, it indicates that physical plugging or scaling of the membrane is taking place. An excessive pressure drop can cause the membrane and/or materials of construction to move and sometimes break, eventually resulting in a complete failure of the membrane.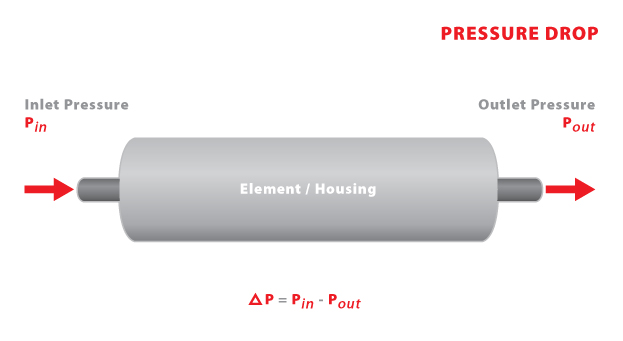
CASE STUDY
Applications
Resources
MEMBRANE RESOURCES
- Definition of a Membrane
- Membrane Materials: Organic vs. Inorganic
- Pressure-Driven Membrane Filtration Processes
- Concentration Polarization in Pressure-Driven Processes
- Degrees of Membrane Separation
- Flux Behavior in Membrane Processes
Module Configurations & Processes
-> View all membrane resourcesTUTORIALS









